Individually scalable: the TwinSAFE architectures
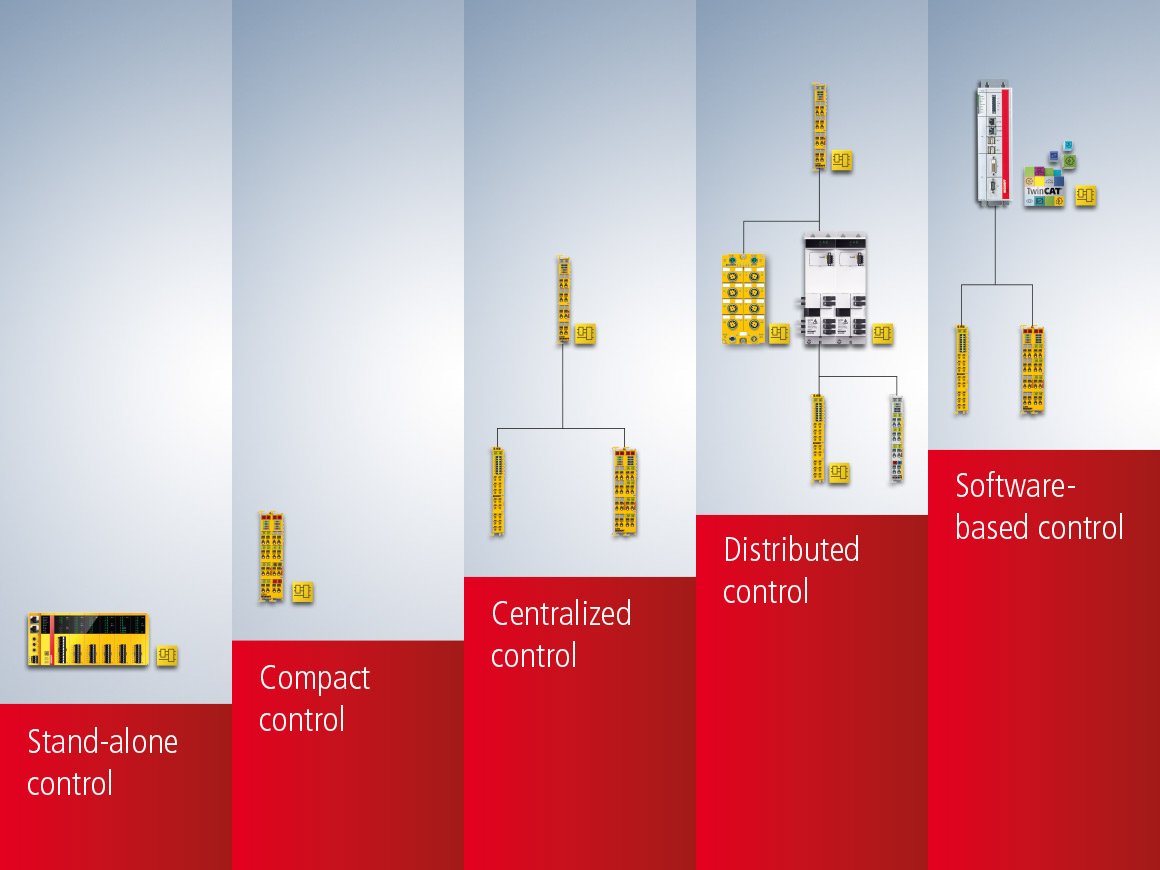
TwinSAFE gives machine builders the possibility to realize the most diverse safety architectures with components in different form factors – from stand-alone control to distributed control, including pre-processing of data directly by I/O terminals, through to system-integrated software-based control for highly complex safety applications. Customers have the benefit of attractively priced, flexible and optimally scalable solutions – and the certainty of being able to meet all safety requirements as needed at all times and in the future, too.
TwinSAFE architectures in detail
TwinSAFE as a stand-alone controller
With the rollout of the two components EK1960 and EP1957, TwinSAFE offers a safety solution for compact applications. These devices can be operated in stand-alone mode without connection to the EtherCAT fieldbus. The safety application is realized on the basis of the safe local inputs and outputs. The stand-alone-capable components can of course also be used, as usual, when fully integrated into the overall system.

TwinSAFE as a compact controller
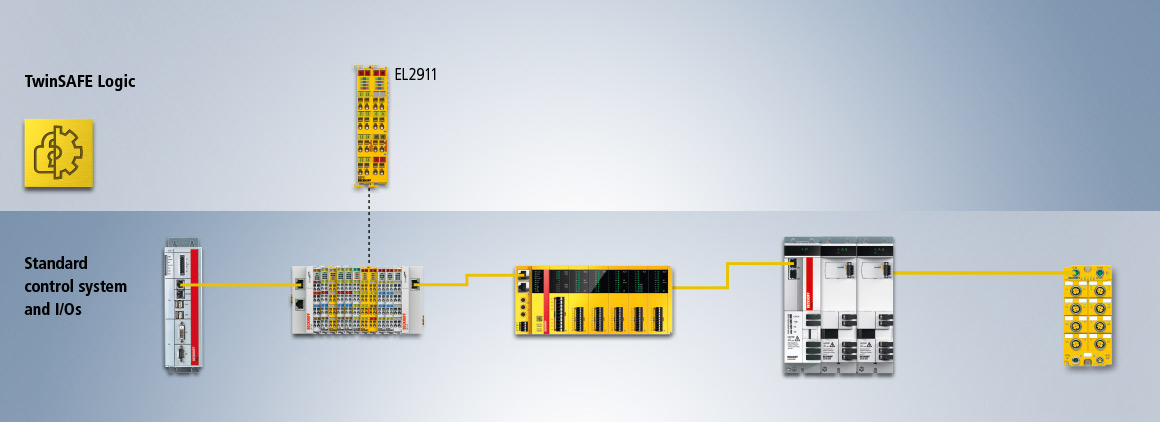
With the integration of the TwinSAFE Logic functionality into all new TwinSAFE components and therefore also into all TwinSAFE I/O components, the potential range of applications for TwinSAFE is significantly extended. In this way, an individual component with local inputs and outputs can be used to realize a safety application (EL1957). As with all TwinSAFE Logic components, communication with existing TwinSAFE components is also possible. In addition to the components represented here, which have both local inputs and local outputs, pure input or output components are also available with TwinSAFE Logic.
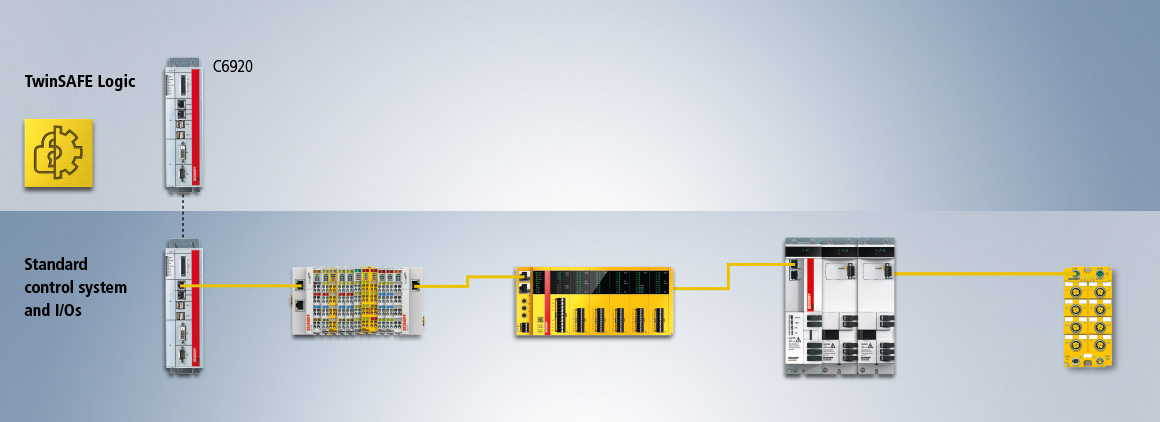
TwinSAFE as a central safety controller
TwinSAFE provides dedicated safety controllers, which can be used for centralized control from a safety technology perspective. These devices themselves do not have local inputs and outputs. Instead, communication relationships are established with 1...n safety-related components, and the safe input and output signals are processed in accordance with the user-defined safety application. The architecture in this case corresponds to the traditional architecture of safety applications. In addition to the dedicated safety controllers represented here, all Logic-capable components can of course also be used in context with a conventional architecture.
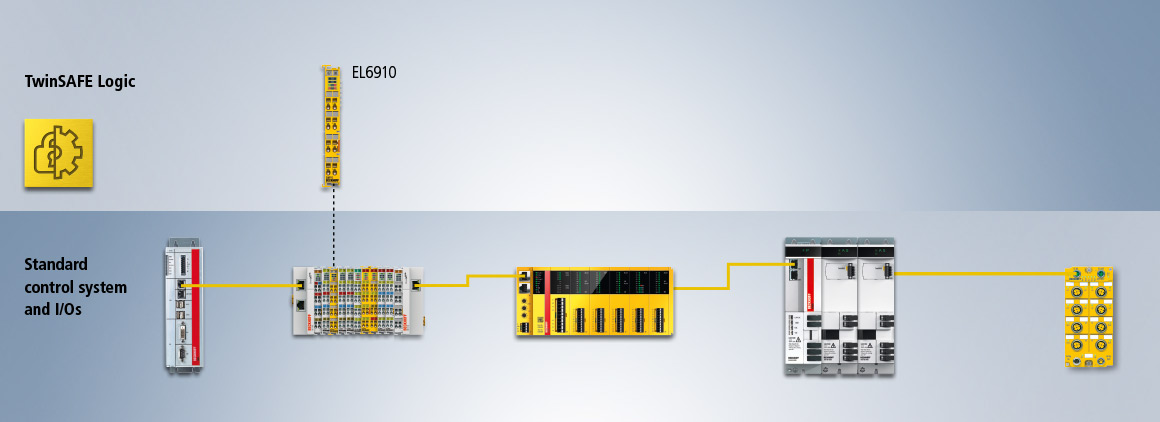
TwinSAFE as a distributed system
Through the integration of the TwinSAFE Logic functionality into all new TwinSAFE components, any distribution or modularization of a safety applications can be realized. In contrast to the traditional architecture, not all safety-related input and output signals have to be transmitted for processing to the central safety controller. The options of distributed control means that, from a safety technology perspective, functionally related components can be modelled by a dedicated safety project. If a system involves an AX8000 group with n modules, for example, where each of these n modules also has to execute safety-related drive functions, then, in the traditional approach, these drive functions have to be controlled individually by the central safety controller. Through the principle of distributed control, on the other hand, one of the modules can now be used as a TwinSAFE Logic, which locally takes over the safety-related control of the other TwinSAFE modules in the group.

Safety control with the standard Industrial PC
With the introduction of the TwinCAT Safety PLC software, TwinSAFE can leverage the enormous performance of standard Industrial PCs in safety control applications. Using an Industrial PC as a software safety controller, even the most sophisticated safety applications can be executed. With the TwinCAT Safety PLC used in a traditional architecture, the overall system is controlled by a single, centralized device, which realizes both the standard functionality and the safety functionality. In contrast to the TwinSAFE hardware components, this safety controller can also be programmed in a standard C derivative with Safety C. This means that safety applications with any level of complexity can be represented. As is typical with TwinSAFE, this architecture can be combined as required with other TwinSAFE architectures.