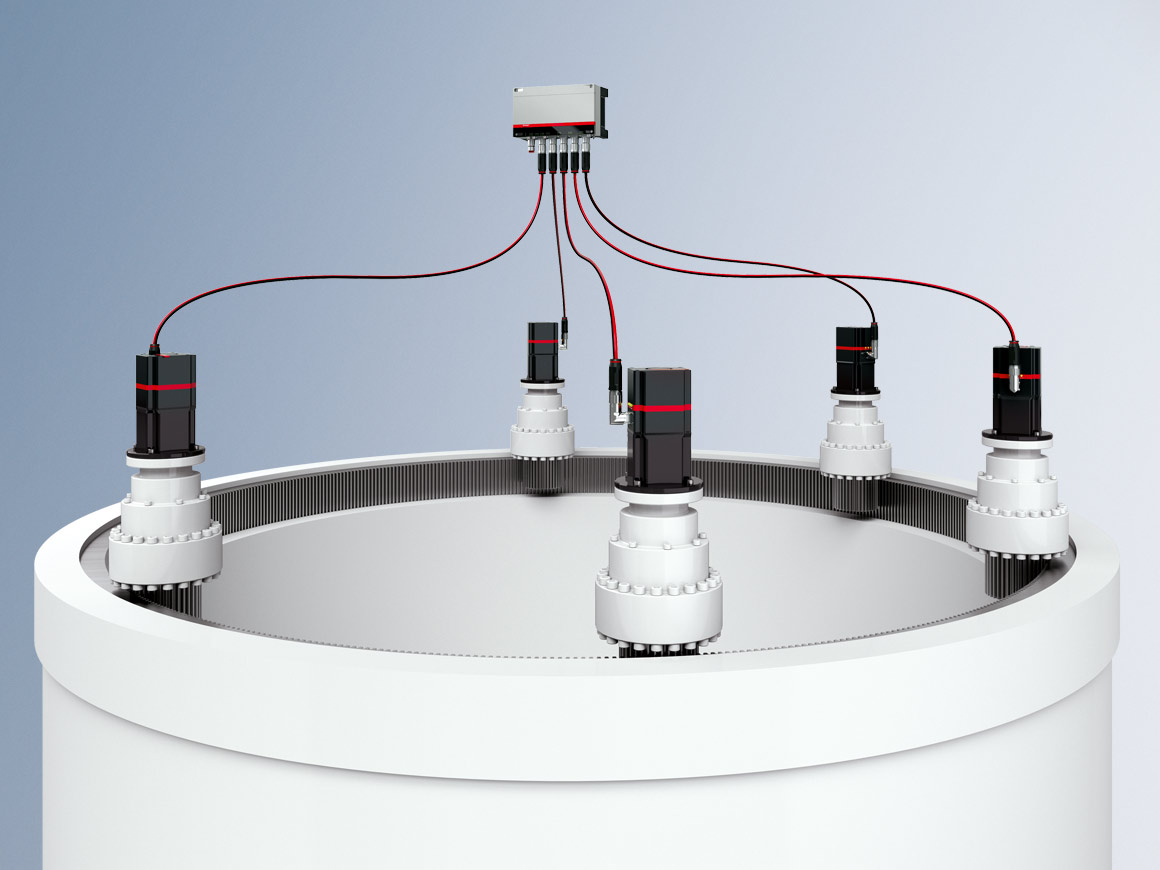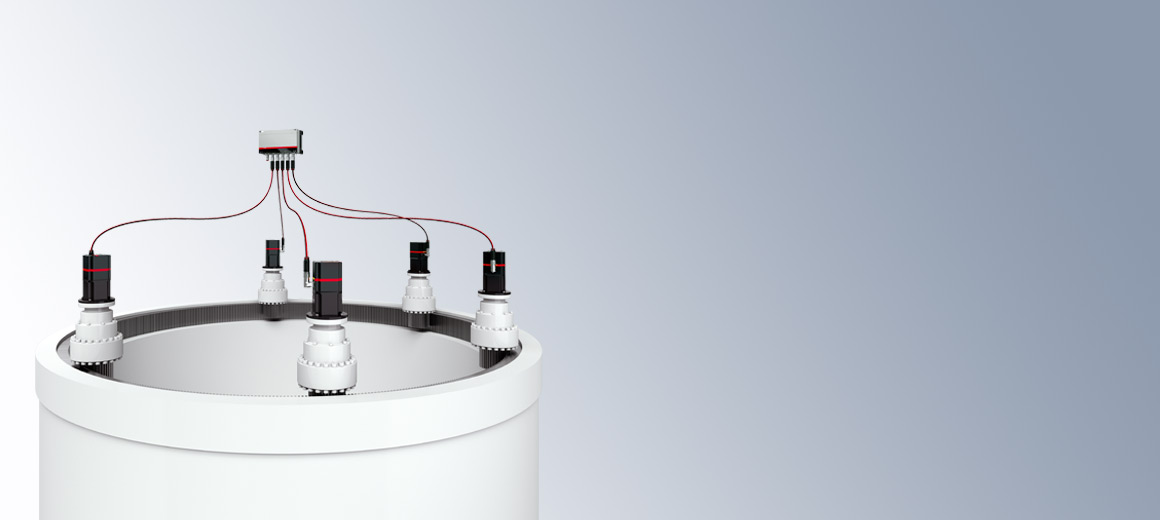

If the wind direction changes, the yaw system rotates the wind turbine rotor optimally into the wind. Apart from the electric drives, hydraulic brake systems are typically also used for this horizontal alignment and locking of the nacelle. However, the permanent use of the brake unit in the active wind tracking results in constant wear in the yaw system, leading to high maintenance expenditure. The use of the existing electric drive systems to develop the required counter-torque and to clamp the mechanism results in less wear and is more efficient.
Traditional drive systems are often based on mains-operated asynchronous motors without soft start, as these are relatively inexpensive. To achieve a safe starting torque in soft supply networks despite that, the motor and the upstream power supply elements are often greatly oversized. However, modern wind turbines offer less and less space for control cabinets. Additional weight and volume must be avoided in particular in the nacelle. These requirements are fulfilled by the AMP8000 drive system with decentralized servo functionality integrated in the motor. Depending on the turbine size and load requirement, the quantity and output of the motors can be adapted for the reliable dimensioning of the drive and braking torques. In comparison with traditional solutions, the servo drive system based on the AMP modules from Beckhoff offers greater efficiency and the safety of adequate breakaway torques even in the case of grid fluctuations.
On account of the wear-prone braking systems, the wind tracking is operated only very sparsely in many turbines. With the new approach, in which the dynamic braking power is achieved without the assistance of the hydraulic brake system, a higher energy yield can be achieved at many wind farm locations through more dynamic wind tracking.
Your advantages at a glance:
- increased energy yield through more dynamic wind tracking
- cost reduction through lower maintenance requirement
- AMP modules reduce installation space and weight in the nacelle
- minimization of the cabling and assembly costs
- optional safety functions, e.g. for system maintenance
- integrated condition monitoring and remote diagnostics
Application reports and brochures
- 02.09.2024 | Application report
Fast control technology reliably compensates for rotor blade movements caused by wind load
Hvide Sande und Seasight Solutions, DenmarkAccording to Danish company Seasight Solutions, the entire industry is talking about a real game changer in the field of wind-turbine installation. This innovative new approach uses human-sized propellers to compensate for wind loads and keep the rotor blades precisely in position in relation to the hub, allowing the huge components to be assembled safely and quickly without hauling ropes – even on stormy days. However, a sophisticated control concept and real-time-capable automation technology are needed to make this possible, which is precisely where PC-based control from Beckhoff comes into play.
- 16.07.2024 | Application report
Transmitting high power efficiently over long distances
MathWorks und Siemens Energy, GermanyWhether from offshore wind turbines on the high seas to the mainland, from wind turbines in northern Germany to industrial sites in the south of the country, or from hydropower plants in Scandinavia to central Europe – high-voltage direct current transmission is used to transmit large amounts of energy over long distances. For its solution, Siemens Energy relies on MATLAB and Simulink from MathWorks and PC-based control from Beckhoff.
- 04.04.2023 | Application report
Precisely controlled stress tests increase availability
IALB, GermanyMajor points of interest to the German energy industry right now include the service life of power electronics in wind turbines along with determining the environmental and load conditions that play a role in this regard. Keen to find answers, scientists at the Institute for Electrical Drives, Power Electronics, and Devices (IALB) at the University of Bremen are working closely with the Fraunhofer Institute for Wind Energy Systems (IWES) to learn more. The data set for this project is determined on an enormous test rig, automated with PC-based control from Beckhoff.
- 02.11.2022 | Application report
Test rig for the next generation of rotor blades
Blaest, DenmarkThe next generation of wind turbines will feature rotor blades measuring 100 m long and counting, up to now making them too big for the existing test rigs at Blaest A/S in Aalborg, Denmark. Along with the construction of a new test hall, the company completely redesigned its control and test equipment: EtherCAT P and a custom measuring amplifier box now replace hundreds of lines and increase accuracy through digitization close to the measurement points. With PC-based control, Blaest is now ready for the future.
- 07.10.2022 | PC Control customer magazine
Wind Compendium 2022
The Wind Compendium 2022, a special edition of our PC Control customer magazine, is a collection of selected application reports about wind power which have been realized with Beckhoff technology. The wide range of applications with varying degrees of complexity will give you an idea of how versatile the solutions are that can be implemented with the open and universal PC- and Ethernet-based control technology from Beckhoff and the benefits it provides.